General Internal Medicine Ultrasound
Modern Ultrasound Diagnostics (Sonography)
- Ultrasound of the Abdominal Organs / Abdomen
- Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS)
- Thyroid Ultrasound
- Breast Ultrasound (Mammography Ultrasound)
- Liver Elastography (Stiffness Measurement of Liver Tissue)
Abdominal Ultrasound
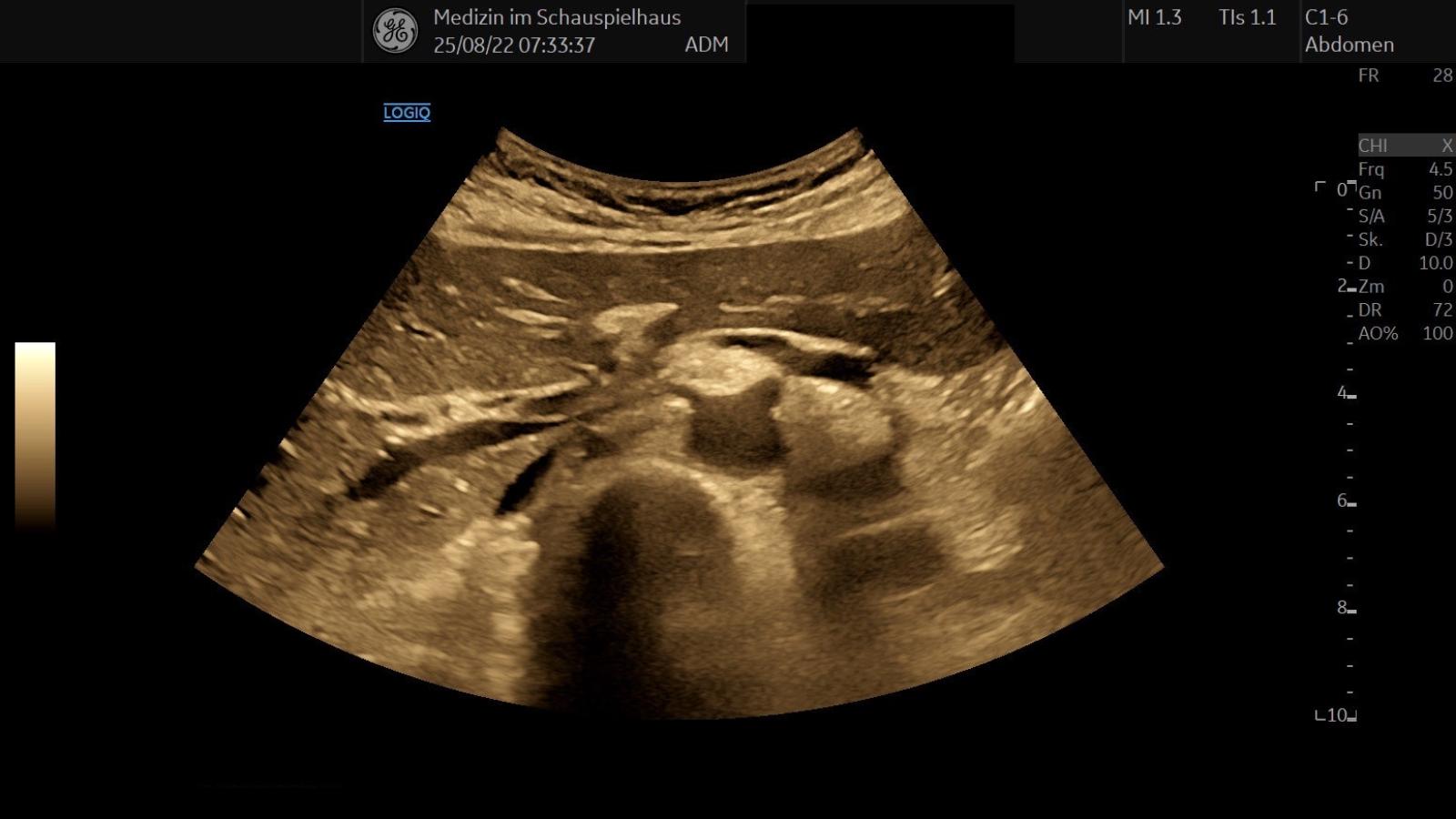
Ultrasound examination can be used to diagnose numerous diseases of the abdominal organs at an early stage, allowing for timely initiation of appropriate treatment. Some examples include:
- Gallbladder: Gallstones, Inflammation
- Liver: Fatty liver, Cirrhosis (including Elastography for measuring liver tissue stiffness)
- Kidneys: Kidney cysts, Kidney stones, Shrinking kidney, Changes due to diabetes, high blood pressure
- Aorta and Abdominal Arteries: Enlargement or calcification with circulation disorders
- Spleen and Pancreas: Diseases of the spleen and pancreas
- Bladder: Residual urine determination
- Prostate: Enlargement, Calcifications
- Uterus: Uterine fibroids (myomas)
Ultrasound can often detect tumor diseases at a very early stage.
The ultrasound examination is non-invasive, meaning no X-rays are used, no contrast agents that could harm the kidneys are required, and the procedure is completely painless. For optimal assessment, the examination should ideally be performed after an 8-hour fasting period with no food or fluids.
Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Examination (CEUS)
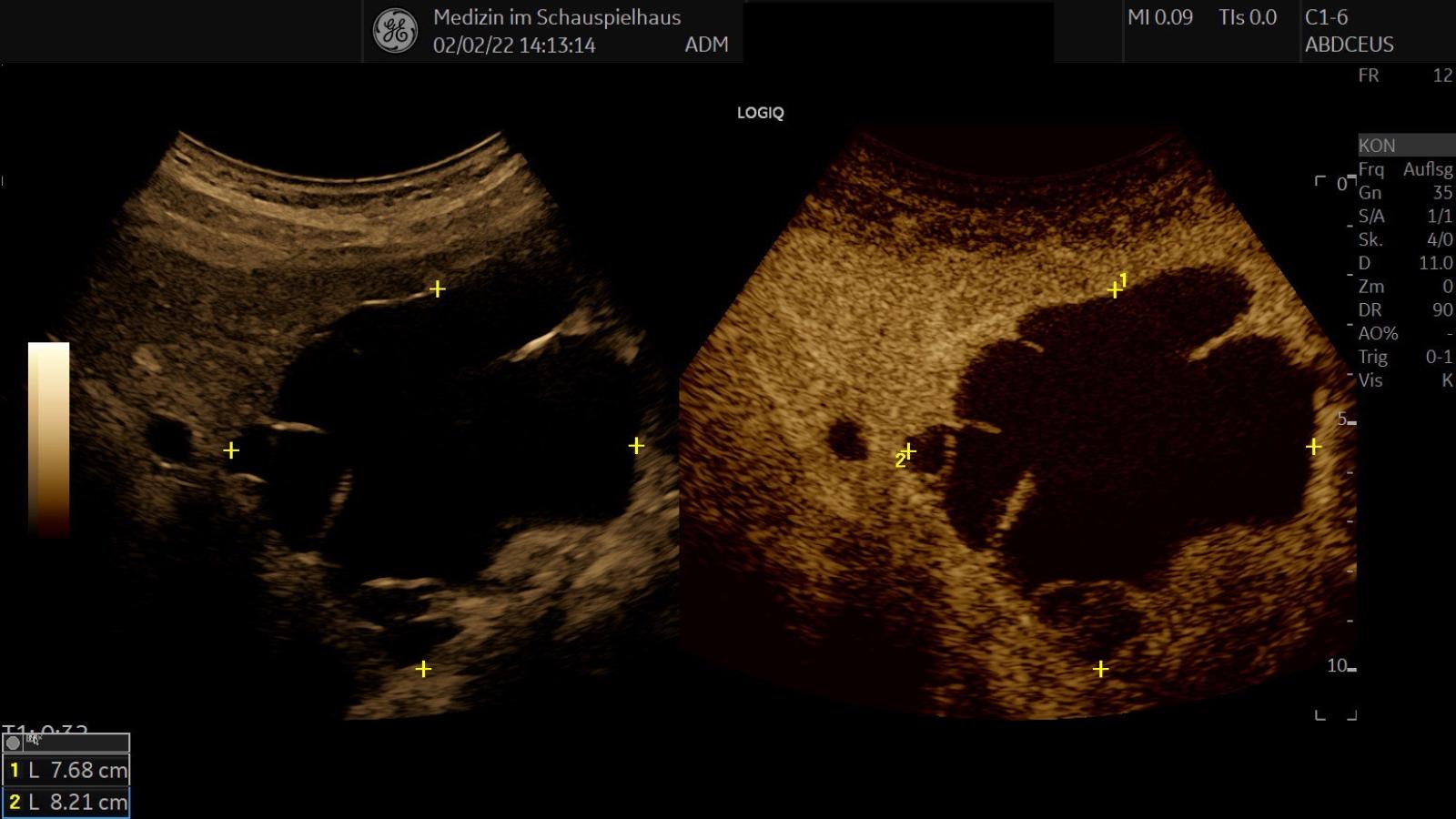
Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) is a new technique in which gas-filled microbubbles are used as a contrast agent. This increases the echogenicity (visibility) of blood and is not associated with any radiation exposure or kidney toxicity (nephrotoxicity). CEUS allows for real-time visualization of blood flow and tissue perfusion in various organs and structures. The combination of ultrasound contrast agents with state-of-the-art ultrasound devices offers a flexible and cost-effective diagnostic method that, compared to existing techniques such as CT, MRI, and nuclear medicine, is often equally effective or even superior in many cases.
We offer the following areas of application for CEUS:
- Evaluation of liver changes, such as hemangiomas, focal nodular hyperplasias, cystic changes, liver carcinoma, or metastases.
- Evaluation of kidney changes, such as complicated kidney cysts (according to the Bosniak classification), angiomyolipomas, benign and malignant kidney tumors.
- Evaluation of pancreatic changes, including benign and malignant pancreatic tumors.
Ultrasound of the Thyroid
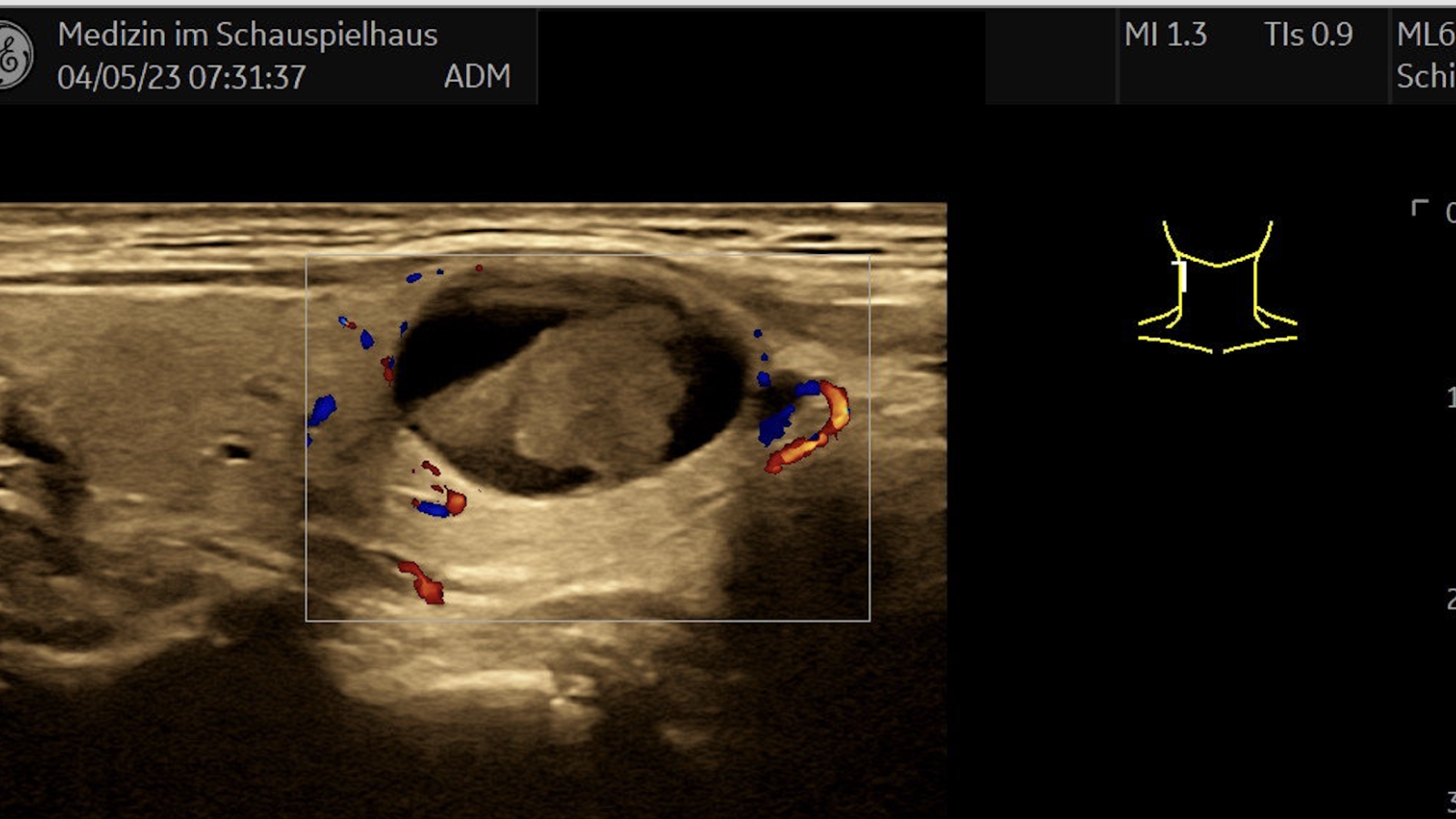
Through the ultrasound examination of the thyroid, the size, structure, and blood flow of the organ can be assessed in cases of dysfunction, abnormalities can be detected, and malignant diseases can be excluded. No special preparation of the patient is required for this.
Breast Ultrasound (Mammary Gland)
Ultrasound examination of the female breast (mammography) is a complementary procedure
to mammography (X-ray examination of the breast).
Advantages of Breast Ultrasound are:
- Painless examination with no radiation exposure (X-rays)
- Palpable findings can be better assessed, e.g., distinguishing between cysts and solid masses
- Highly suitable for women under 30 years of age with breast pain (mastodynia)
Liver Elastography
(Stiffness Measurement of Liver Tissue)
Elastography generates shear waves in the liver using acoustic force from a focused ultrasound beam and measures the propagation of these shear waves, as well as their speed. This provides stiffness measurements of liver tissue. In chronic liver diseases, liver tissue can die and be replaced by scar tissue, which is denser and less elastic than the original liver tissue. Elastography is particularly useful for detecting liver fibrosis or cirrhosis.